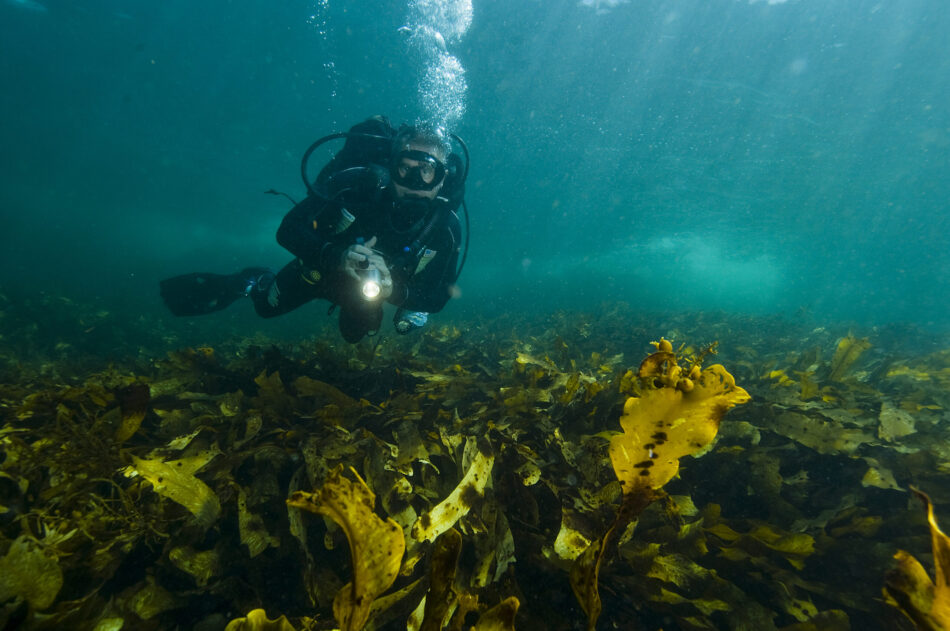
Ministry of Heritage and Tourism (MHT) has established a directorate for the underwater antiquities, the first unit of its kind in the GCC region
As it abounds with various underwater and submerged cultural heritage sites bearing witness to its role as an axis of the human civilisations since the early prehistoric periods, the Sultanate of Oman is now keen to promote tourism centred around its underwater heritage.
According to a press statement, since several ships, coastal human settlements and aircrafts containing collectibles with cultural and economic significance sank in the Omani territorial waters, the Ministry of Heritage and Tourism (MHT) has established a directorate for the underwater antiquities, the first unit of its kind in the GCC region.
Oman’s maritime history dates back to the 3 BC
“The underwater archaeological sites and ships are a source of precious historical information as they contain antiquities of human existence. The archaeology aims to analyse the antiquities, identify the origins and the development of civilisations,’’ says Ayyoub Nagmoush Al-Busaidi, Director, Directorate of the Underwater Submerged Antiquities, Ministry of Heritage and Tourism (MHT).
“Underwater archaeology is a scientific discipline that deals with the studying sites, man-made objects, human remains, and submerged landscapes. This science should be placed within its broader framework of marine archaeology, which studies human relationships with oceans, lakes, and rivers, while complementing it with navigation,” he adds.
Several techniques have been used in the underwater archaeological survey
The statement adds that in 2012 the MHT launched a programme aimed at identifying resources and components of these antiquities, enumerating them, and determining their nature, and protecting them from illegal trade and natural factors, he added. The department is now working on formulating rules for protection, management, employment, conducting surveys, excavations, restoration, preserving, documenting archaeological sites, analysing the results, and presenting them to the local and international community.
The statement goes on to say that Oman’s maritime history dates back to the 3 BC, when commercial activity flourished in Mesopotamia and the Nile River Valley. After Omanis gained good expertise in navigation in the 18th century, Muscat emerged as one of the most important trade centres in the Indian Ocean, it adds.
Several techniques have been used in the underwater archaeological survey. Most effective of all is an advanced navigation system by means of GPS satellite positioning, and special ships equipped with remote sensing devices such as magnetometer, side scan sonar, multi-beam and sub-bottom profiler in addition to the marine geophysics equipment.
All data, pictures and drawings will be collected and documented by computers for processing and later dealing with the site of the finds and archaeological remains in accordance with the data that was concluded.

The archaeology aims to analyse the antiquities, identify the origins and the development of civilisations
“The department is working to give a character to activities undertaken in underwater antiquities in Oman. Research has been conducted in the framework of underwater archaeology, in accordance with three axes—surveys, excavation, restoration and preservation. After extracting the antiquities, restoration and preservation work of the objects containing metal and glass must be carefully dried. As these artifacts have been wet for many years, they must first be preserved, to prevent decay or damage,’’ adds Al-Busaidi.
The statement adds that the ministry secures the preservation of such archaeological finds, conducts surveys, excavations, restorations, preserves and documents archaeological sites, including training cadre on methods used in restoration, preservation, and documentation.




















